Knee Arthritis : Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Knee arthritis is a common joint condition where the cartilage in your knee gradually wears down, reducing the joint’s ability to move smoothly. Cartilage is a tough, slippery tissue that cushions the ends of the bones and allows pain-free motion. When it deteriorates, bones can rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
This condition affects people of all ages, though it is more common in older adults. It can also develop after knee injuries, surgeries, or repetitive stress from activities like sports or heavy labor. Obesity and genetics can further increase the risk.
If left untreated, knee arthritis can lead to chronic pain, difficulty performing daily tasks, and decreased quality of life. Early recognition and proper management — through lifestyle changes, physiotherapy, medications, or surgery — can slow progression, relieve pain, and improve joint function.
Key features of knee arthritis :
- Pain, especially during or after movement
- Swelling and warmth around the knee joint
- Stiffness, particularly after rest or in the morning
- Reduced flexibility and mobility
- Grinding or popping sounds in the joint
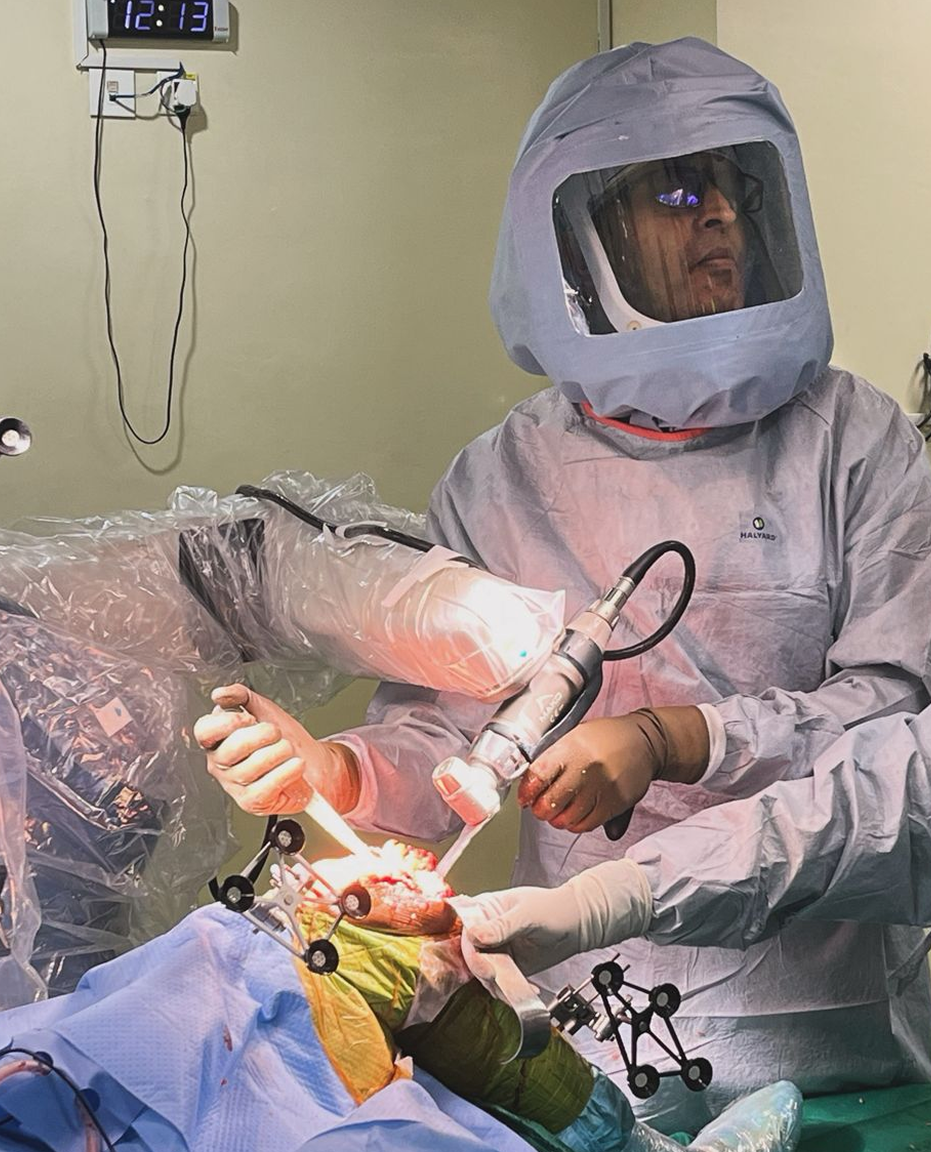
The Problem
Knee arthritis is more than just knee pain — it gradually affects how you move, work, and perform daily activities. The joint may become stiff, swollen, and less flexible, making simple tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or bending difficult. Over time, this can impact independence and overall quality of life if not addressed early.
- Pain and discomfort : Often worsens with activity, sometimes present even at rest in advanced stages.
- Stiffness and swelling : Makes bending, straightening, or standing for long periods difficult.
- Reduced mobility : Everyday tasks such as walking, climbing stairs, or squatting become challenging.
- Impact on lifestyle : Without treatment, it can reduce independence and overall quality of life.
The Incidence
Knee arthritis is one of the most common joint conditions worldwide, affecting millions of adults. It becomes more prevalent with age, especially after 40–50 years. Other factors, including obesity, previous knee injuries, and family history, increase the likelihood of developing arthritis. Early detection is important because timely intervention can slow progression, reduce pain, and maintain mobility.
- Millions of adults worldwide are affected.
- Risk increases with age and lifestyle factors.
- Early care can prevent severe joint damage.
AREA OF EXPERTISE
- Robotic and non-robotic knee replacement surgery
- Fracture surgery of upper and lower extremities
- Geriatric hip fracture surgery
- Knee arthritis treatment
Why Does Knee Arthritis Happen?
Knee arthritis develops due to a combination of wear-and-tear, injury, genetics, and lifestyle factors. The cartilage that cushions the knee joint gradually breaks down, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Natural wear and tear : Cartilage loses elasticity over time, leading to degeneration.
- Injury history : Previous fractures, ligament tears, or meniscus injuries can trigger arthritis later.
- Excess weight : Adds extra stress on the knee, accelerating cartilage breakdown.
- Genetics : Family history can increase susceptibility.
- Repetitive stress : Jobs or activities involving frequent kneeling, squatting, or heavy lifting contribute to joint damage.
Early evaluation and treatment can improve mobility, reduce pain,
and enhance your
quality
of life. Our experts are here to guide you through every step.
Solutions for Early Arthritis
For mild or early-stage arthritis, the goal is to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further damage. Non-surgical treatments are usually effective when implemented promptly.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintain a healthy weight and stay active with low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Physiotherapy: Strengthen surrounding muscles to support and stabilize the knee.
- Pain management: Use medications such as topical or oral pain relievers under medical guidance.
- Pain management: Use medications such as topical or oral pain relievers under medical guidance.
- Supportive aids: Braces, orthotics, or walking sticks can help reduce strain on the joint.
Solutions for Late Arthritis
In advanced cases, when pain and mobility limitations persist despite conservative treatment, surgery may be recommended. Surgical options aim to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve quality of life.
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): Replaces the damaged joint to relieve pain and restore function.
- Partial Knee Replacement: Suitable when only a single compartment of the knee is affected.
- Osteotomy: Realigns the bones to reduce pressure on the damaged part of the knee.
Surgical treatment can significantly improve mobility, relieve pain, and help patients return to normal daily activities.
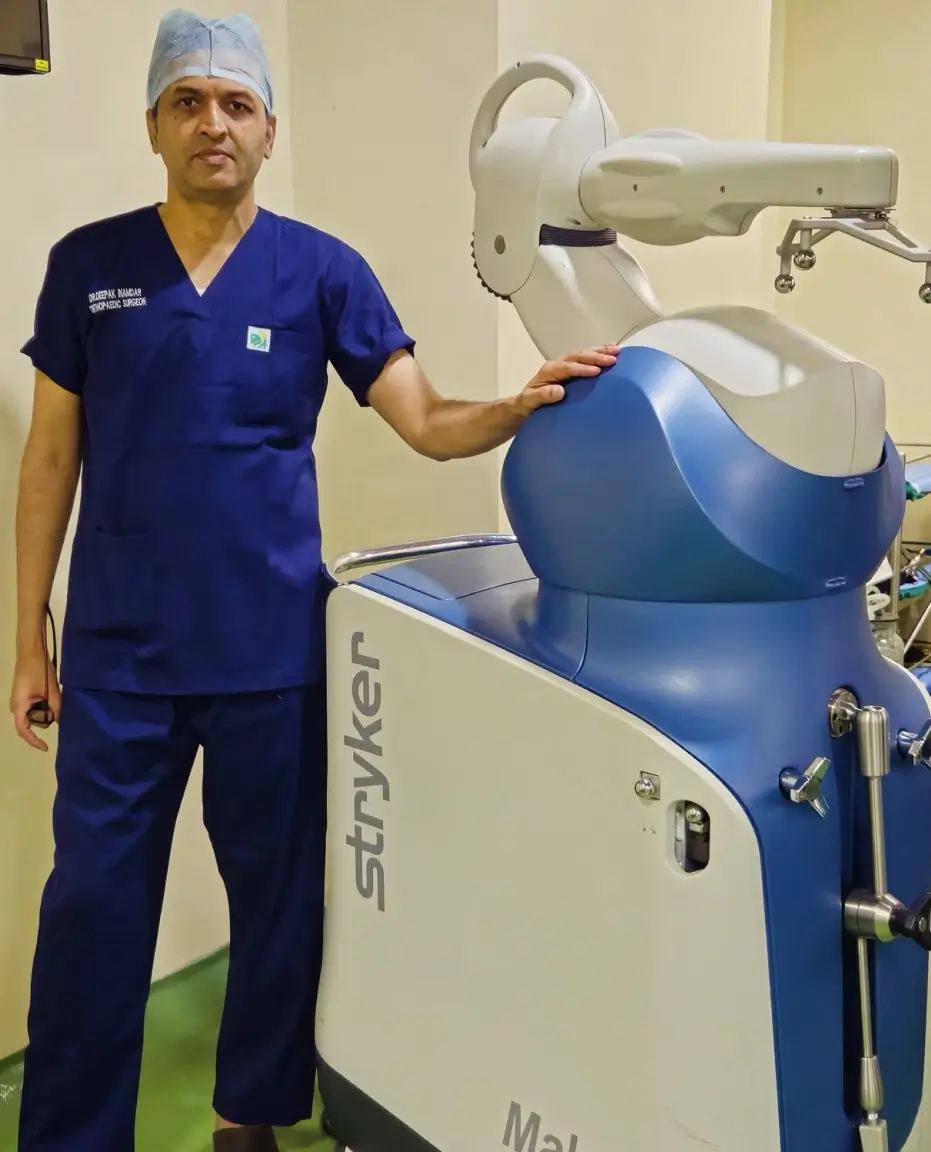
Thinking About Joint Replacement Surgery? Get Expert Opinion from Dr. Deepak Inamdar!
 Surgeon for reputed orthopedic surgeons
Surgeon for reputed orthopedic surgeons